The H2 Economics syllabus is more difficult than its H1 counterpart, with additional content and topics within its three main themes. Many students struggle to understand the more complex elements, and have trouble coming up with the right answering techniques for them. The extra emphasis on essay writing also makes H2 Economics particularly difficult, and developing the appropriate skillset to deal with this is vital.
Follow us as we break down the components of the H2 Economics Syllabus, and explain what students will need to prioritise.
Components of H2 Economics
Both Economics syllabuses share the three central pillars of economics.
The Central Economic Problem involves the issue of scarcity. It encourages students to explore how choices are made in the face of limited resources, and the consequent need for allocation.
The Markets segment involves analysing the dynamics of demand and supply under various market structures. Students analyse market interactions and how these affect resource distribution, and then evaluate the efficiency and equity of markets. H2 Economics covers Firms and their decisions as part of this topic.
The National and International Economy introduces macroeconomic concerns such as economic indicators, policies, and objectives. It imparts a global perspective by considering the impact of national economic activity on economic performance and societal well-being. The H2 Syllabus adds in the Circular flow of income as well as Globalisation, International Trade and Economic Co-operation.
Theme 1: The Central Economic Problem
The Central Economic Problem revolves around unlimited wants and limited resources. This scarcity is the basis for all of economics, and this theme forms the foundation for microeconomic and macroeconomic analysis further in the syllabus. Some important concepts within this theme are:
Economic agents—be they individuals, businesses, or governments—engage in a decision-making process that attempts to be rational and systematic. These decision-makers gather and analyse information, evaluate the benefits and constraints, and consider various perspectives before arriving at choices. Such decisions aim to maximise economic welfare but can carry both intended and unintended consequences.
- Information Gathering: Collecting relevant data
- Evaluation: Assessing benefits, costs, constraints, and perspectives
- Final Choice: Making a decision aimed at maximising welfare
- Demand: The quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase at different prices.
- Supply: The quantity of a good or service that producers are willing and able to offer for sale at different prices.
- Demand and Supply Analysis and its Applications: Further analysis of the law of supply and demand.
- Government Intervention in markets: How Taxes, subsidies, and other forms of price control can affect the market.
Students aim to understand the objectives, cost & revenue structures, and decision-making strategies of Firms. These firms, as fundamental economic units, primarily aim to maximise profits, a goal achieved by ensuring that the difference between total revenue and total cost is maximised.
Objectives of Firms: Firms must ensure that they make a profit. This profit-maximising output is identified at the point where marginal revenue (MR) equals marginal cost (MC), and where MC is rising.
Cost and revenue: Students learn about the cost and revenue that firms encounter in both short-run and long-run scenarios. The syllabus explores internal and external economies and diseconomies of scale, linking them to the long-run average cost of production. Students gain a basic understanding of how firms achieve efficiency and scale their operations.
Decisions and Strategies: Firms’ decisions and strategies form a critical part of the syllabus, highlighting how firms engage in various tactics to enhance revenue and reduce unit costs. Strategies such as growth, diversification, shut-down, price competition, third-degree price discrimination, innovation, and marketing are examined. These decisions and strategies are crucial for understanding how firms interact with the market and influence efficiency, consumer welfare, and the competitive landscape.
Microeconomic objectives are goals held by individual firms or governments, to improve market outcomes. Policies are implemented to manage or influence these objectives, dealing with issues like efficiency and equity.
Policies may include price controls, subsidies, or taxes, each with the aim of correcting distortions in the market. Students will learn about topics such as:
Market Failure and its Causes: What happens when a market fails to allocate resources effectively, and the reasons for it taking place, such as Externalities, public Goods, and Information asymmetry.
Microeconomic Policies: Competition policy, Regulatory policy, and Redistribution policy.
Theme 3: The National And International Economy
The final theme in the H1 Economics syllabus revolves around The National and International Economy, and the macroeconomics that affect it. This topic covers the analysis of aggregate demand and supply, indicators affecting the standard of living, prevailing economic issues, and the implementation of various macroeconomic policies. It also covers the impact of globalisation on government decisions and macroeconomics.
Macroeconomic analysis provides a comprehensive view of the economy by considering broad factors and behaviours that affect the entire nation. It facilitates an understanding of how different sectors of the economy interact and perform collectively. Students are taught to understand Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply.
Aggregate Demand (AD) represents the total demand for goods and services within a nation at a given overall price level and in a given time period. Aggregate Supply (AS), conversely, reflects the total output an economy can produce when it is most efficient. Together, these determine the national economy’s price level and Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
H2 Students are also taught about Circular Flow of Income, a model that illustrates the continuous movement of money among different sectors of an economy. This concept serves as a framework to understand how income circulates through various economic agents, primarily households and firms, and how it facilitates the exchange of goods and services.
The second theme is to understand the Objectives and Policies behind macroeconomics. These include:
- Standard of Living and Macroeconomic Indicators: The priority that economies give to improving the standard of living, and how this standard is affected by the ability to meet macroeconomic objectives.
- Consequences of Macroeconomic Issues: Examples such as Unemployment, Undeisrable Economic Growth, Price Instability.
- Macroeconomic Policies: How Fiscal, Supply-side, and Monetary policies are all able to achieve macroeconomic objectives when successfully undertaken by the government.
The largest difference between the H1 and H2 version of this topic is the focus on globalisation. Students carry out an in-depth exploration of Globalisation, International Trade, and Economic Co-operation. This topic introduces globalisation as the intensification of cross-border trade in goods and services, as well as a source of of capital and labour.
- Free Trade: The topic covers the basis of free trade and specialisation, as well as the costs and benefits of it. There’s particular coverage of consumers, producers, and the government’s impact on it.
- Protectionism: Protectionism refers to the economic policy of restricting imports from other countries through methods such as tariffs, import quotas, and a variety of other government regulations. These measures are designed to protect domestic industries from foreign competition by making imported goods more expensive or limiting their quantity. The topic analyses the underlying aim of protectionism.
Deciphering The H2 Economics Syllabus
The H2 Economics syllabus can be particularly challenging, and requires a firm understanding of the basic economic principles. Students have to learn how to assess markets, make coherent economic arguments, and then apply these theories in an examination setting.
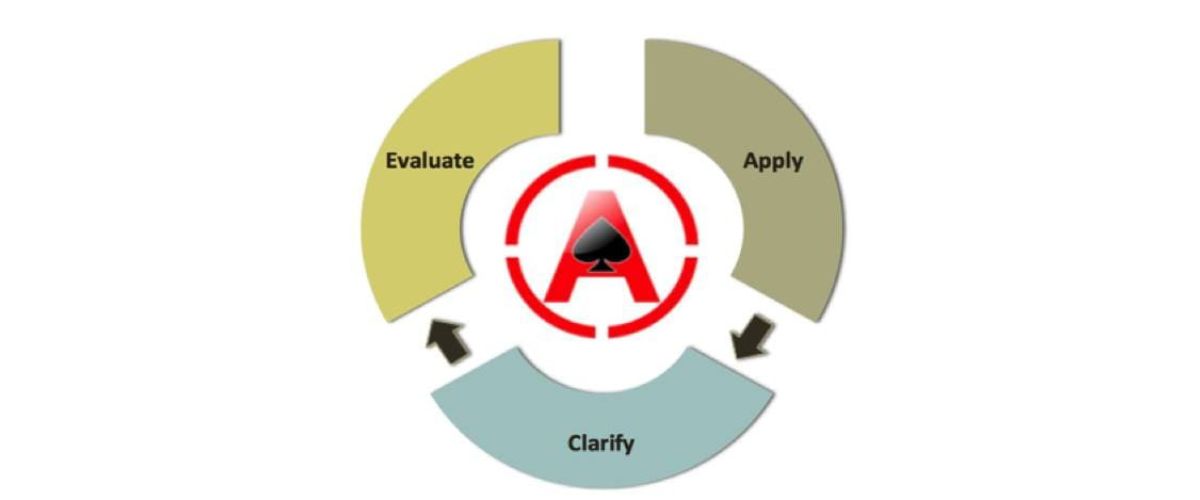
ACE Framework
For students finding the breadth and depth of these topics daunting, AceYourEcons stands at the ready to help demystify these key concepts. Through our intensive Economics Tuition program, students can receive the guidance they need to keep up with this difficult syllabus. Through our proprietary ACE (Apply, Clarify, Evaluation) Framework, we aim to help your child nurture their critical thinking skills, and help them understand fundamental economic concepts. In our lessons, we strive to build:
Knowledge and Understanding: It’s essential for students to have a clear comprehension of economic theories and principles.
Application Skills: Students must learn to apply concepts to solve problems and analyse economic situations.
Interpretation and Evaluation: Skills in interpreting economic data and critiquing economic decisions are crucial.
Developing Case Study Skills
Learning how to analyse past case studies is vital in H1 Economics. At AceYourEcons, we make sure to place significant emphasis on case study skills and answering techniques. The ability to apply this theoretical knowledge is a key part of examinations, so we ensure that our students are able to critically analyse and answer the text. These skills are vital not only in Economics, but in a broader academic context.
Unlike traditional methods that may rely heavily on rote memorisation, there’s a greater emphasis on:
Application from Data and Extracts: Students are trained to adeptly use information provided in case studies to support their analysis and arguments. This requires not only an understanding of the data presented but also the ability to correlate it with economic theories and concepts.
Minimising Rote Learning: Our approach de-emphasises memorisation in favour of understanding and application. This shift away from rote learning encourages students to engage more deeply with the material, fostering a more meaningful and lasting comprehension of economic principles.
Critical Thinking and Analysis: By focusing on case studies, students are compelled to think critically and analytically, skills that are invaluable in their professional futures.
Through our targeted instruction and the ACE Framework, we aim to equip students with the skills necessary to excel in the H1 Economics syllabus. Our regular usage of case study essay question analysis helps students cultivate an understanding of the syllabus without excessive memorisation.
Prioritising Exam Preparation.
Recently, mid-year exams have been removed from the JC1 curriculum. A common concern about this change is that it places substantial emphasis on the promotional examination at the end of JC1. Delayed discoveries of conceptual gaps are likely more consequential and may result in a higher risk of being retained in JC1. At such, our teaching methods revolve around cultivating good exam practice and habits in our students. Through the rigorous adoption of weekly essays and case studies, we ensure that students are perpetually prepared for the high-stake exams at the end of the year. We also conduct two mock exams and full assessments monthly, to regularly gauge the learning progress of each student and keep them ready for promotional and A-Levels examinations.
Master H2 Economics with Aceyourecons
Achieving success in H2 Economics requires a strong understanding of the subject matter and the ability to apply economic concepts to real-world scenarios. Whether you’re a Junior College student balancing multiple subjects, or a Private Candidate who may require a more tailored guidance, we’re ready to provide the right level of guidance.
We offer a tailored Tuition Approach designed to cater to the diverse needs of students. Our tuition programme meticulously focuses on examination techniques that help learners secure their desired outcomes and learn how to analyse economic issues.
Rigorous Curriculum: Our Economics curriculum is strategic, ensuring that students engage with a variety of case studies and essay questions.
Skill Development: Students develop critical analysis, logical argumentation, and coherent essay writing skills. They gain the ability to evaluate perspectives and understand the three major themes in economics.
Contact us today to find out more about our tuition programs, and help your child prepare for their Economics exams today.